In the fast-paced and ever-evolving landscape of modern business, customer satisfaction and loyalty are paramount. As businesses strive to stay ahead of the competition, one term that has gained significant prominence is "user experience" (UX).
It encompasses the overall interaction a person has with a product or service, and it plays a crucial role in shaping perceptions and influencing decision-making. However, beyond the generic term "user experience," businesses use various other terms and concepts to delve deeper into this multifaceted aspect of their operations. The question naturally arises: What is user experience called in business?
What Is User Experience (UX) Design?
User experience (UX) design is the method that design teams use to make goods that give users meaningful and valuable experiences. UX design is the process of planning the whole process of getting and using a product. It includes branding, style, usability, and function.
Making the software easy to use is only one part of designing an experience. You also have to think about the other experiences that go along with the product, like the marketing campaign, the packaging, and the help after the sale.
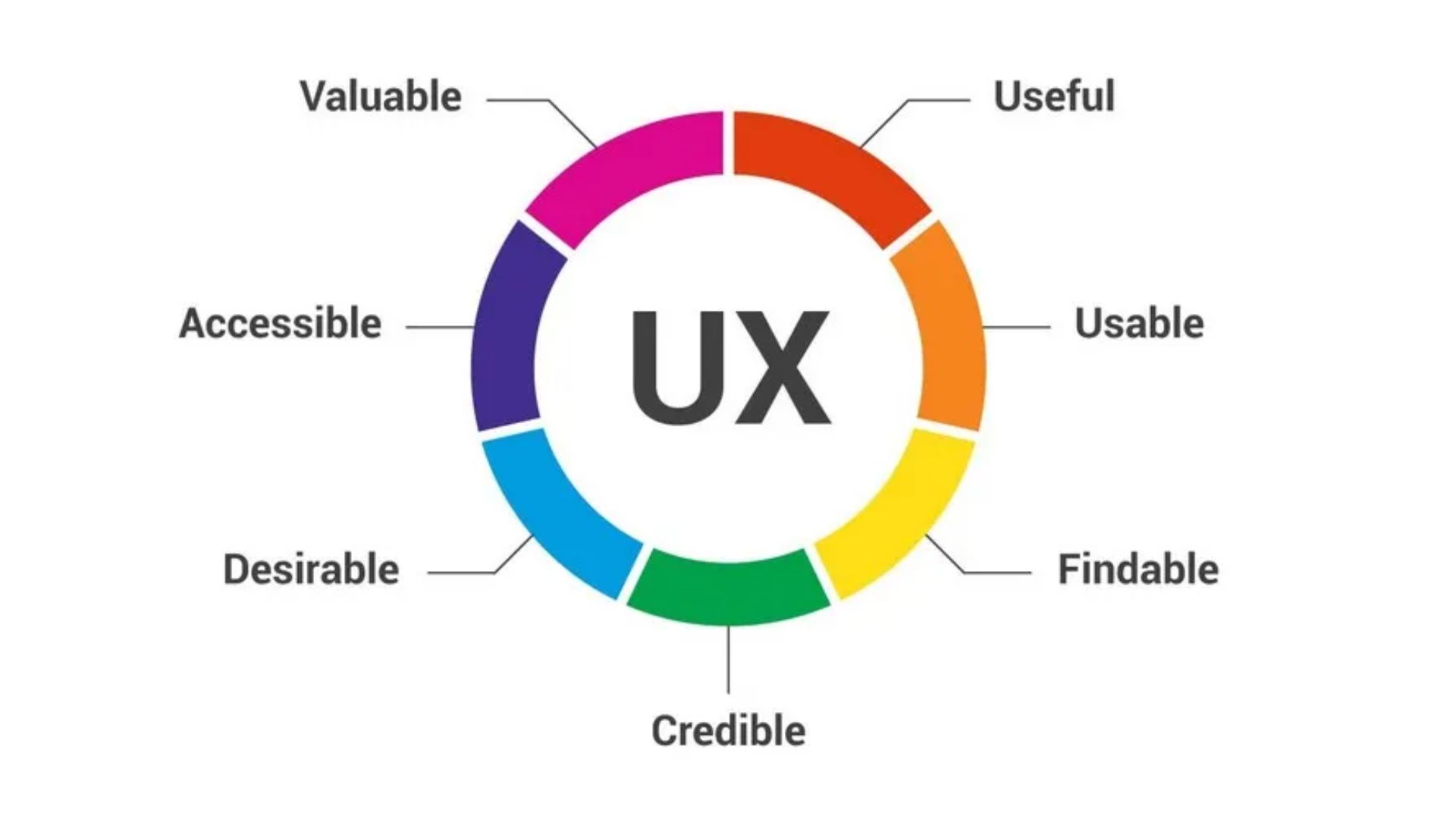
Most importantly, UX design is about making solutions that meet wants and ease pain points. In the end, nobody will use something that doesn't do anything. To put it simply, UX design helps creators make things that are useful and easy to use. The following six areas are all part of UX design.
- Being useful- The product must meet a real need of the person who is using it.
- Being desirable- Visual design, for example, must be used to make the product look reasonable and uniform.
- Easy to use - The product needs to be easy to use and have features and functions that people are already familiar with.
- Easy access- Everyone must be able to use the goods, even people with disabilities.
- Ability to support- Users should be able to quickly and easily fix any problems with the product if it comes with good help.
- Having credibility- The goods must be reliable, like coming from a well-known company or being carefully secured.
Why Is UX Design Important?
When trying to get and keep people or customers, the user experience is significant. Think about any physical or digital item. If people don't need the product, don't like using it, or can only comfortably use it with a little trouble, they will stop using it and switch to a competitor's product instead.
This could not be good for the business's image and income. On the other hand, a good product that meets a clear need and provides good performance and support can bring in more customers, improve the company's image, and make people more loyal to the company and its brand.
For most businesses, a good user experience can be essential to their success. This is because users are what bring in money through products or services. So, project managers and people who have a stake in the product should pay attention to UX problems like usability testing or user acceptance testing.
What Does A UX Designer Do?
A UX designer uses a variety of tools, such as graphic design, layout, language, testing, and user study and testing. They might write code (usually in HTML/CSS), make wireframes and models, design logos and buttons, or even write the text that is in the product.
To learn more about the customer experience, UX designers may interview customers or take part in them. This helps them figure out what matters to customers and how they do important tasks (either with the product or another way). When the product is finished, UX will often be in charge of user testing. They will write the scripts, look over the results, or even run the tests themselves.
Once the product is out in the world, UX designers will use analytics to learn more about the customer journey and try to figure out which processes work well and where stories are running into problems.
UX designers also set the "visual grammar" for a product by making or choosing the fonts and icons that explain the brand and give users visual cues that they will get used to over time. They will also make sure that the language on the site is explicit and valuable to the audience, that it stays the same, and that it is easy to understand throughout the whole customer journey.
User Experience As A Business Process
As a business process, User Experience is made up of the tasks, tools, and methods that companies use to make digital goods that great users love. The customer is at the center of the UX process, which encourages collaborative design, tests assumptions, and works best when done over and over again.
Any company that deals with customers digitally these days needs to have good user experience skills. This is true for mobile apps, websites (for customers and business partners), electronic booths, ATMs, and more. 74% of companies think that user experience is important for making more sales.
When businesses try to give users a good experience, they try to control how they connect with and think about their digital products. Those thoughts and feelings should lead to good emotions and feelings that will make customers more loyal to the brand and encourage them to buy from it again.
Who Is Responsible For User Experience In A Business?
Most of the time, user experience designers are in charge of most businesses. However, many jobs and teams are responsible for making sure that users have great experiences. A UX designer works with people like copywriters, web developers, art directors, and visual designers.
Working with all of these different experts is one of the hardest things for UX designers to do. UX designers also show products to real people and get their comments on how to make the experience better.
UX Designers
UX designers are the ones who work directly with users. These workers are experts at making interfaces that look good, work well, and are easy for people to use.
They use user-centered design principles, test the usability of their designs, and make changes to them over and over again to make sure the final result meets users' needs. UX designers are significant for turning business goals into solutions that work, look good, and meet those goals.
Product Managers
Product managers connect the goals of the business with the needs of the end customer. They are in charge of making the product roadmap and work closely with developers, UX designers, and other partners to make sure the product meets both user needs and business goals.
Product managers make choices that affect the whole user trip. They do this by looking at things like the user interface, features, and functions.
Developers
Developers make the user experience real, while UX designers only think about it. Developers have more to do with the user experience than just writing code.
They need to know how to create the user interface and work closely with UX designers to make sure that interactions work smoothly. Code that is clean and works well is essential for making sure that the digital experience fits the design, which significantly increases user satisfaction.
Customer Support Teams
User experience isn't just during the planning or pre-purchase stages; it also includes interactions that happen after the purchase. Customer support teams are critical to user happiness because they answer questions, deal with concerns, and solve problems.
They are the direct link between the company and its customers, giving the company helpful information about what might need to be fixed. These teams help users have a good experience by providing quick and helpful support.
Data Analysts
Today's business world is based on data, and data analysts are very important for knowing how users behave. They give helpful information about how well different parts of the user experience work by looking at metrics like bounce rates, conversion rates, and user involvement.
Businesses can use these insights to make data-driven improvements to their goods and services, which helps them make decisions.
Marketing Teams
A person's experience with a product or service starts before they even use it. Through branding, messages, and promotional activities, marketing teams have a significant impact on how users think about and expect from a product or service.
The foundation for a good user experience is consistent and positive messaging. This makes it possible for a smooth trip from awareness to conversion.
Leadership And Executives
In the end, a company's leaders and executives are responsible for creating an atmosphere that puts users first. Leaders set the tone for the whole company by putting user experience first in group goals and resource allocation.
When leaders support values that put the user first, they spread throughout the company and affect how decisions are made at every level.
Underlining The Advantages Of UX Design
Greater Insight And Value
Being able to see a lot about the product being built helps you know what you're doing. Sometimes, you want to reach out and touch the sky. But we often need to remember what our means are, like our salary.
Lesser Development Time
It might be tough for you to believe. Do-overs are very possible if you still need to do your homework right, though. This is why it's so important to get the right website design or clever mobile app design.
The name for this is prototyping. It helps you figure out what to build on, what the customer wants, how the business works, and what the product is.
Focus On Customer-Centricity
In the end, it's all about what the person wants and how important that is. You can test a segmented user group with the help of a good mockup. This helps you figure out how well the final product will do in the market.
It tends to do that with UI/UX design, whether it's a web design or a sample for a mobile app. It helps you figure out what's important and how well the product you created will do in the market.
Upholding Company's Image
It might take a while to stand out in a market with so much competition. But it would help if you always thought about your company's logo, colors, and overall theme when writing. Then, come up with a design idea that takes all of these things into account.
You want to make a product that fits with how your business is seen. Or you're a new business trying to find a spot in the market. In this case, your output will be the clear path that other parts must follow.
Lower Support Costs
This may seem like a vague idea, but it is a great design concept and execution. A well-built product can move on to the ongoing support and operations part as soon as it goes live.
This is an essential part of helping a product that has a lot of bugs and questions from users. You must fix these problems quickly so that customers can still get the goods.
Best Practices Of UX Design
Because they work with such a wide range of people, UX designers usually have access to everyone in the company. Still, good UX designers should follow a few rules that are true in all fields. Because of a bad customer experience, 89% of people switched to a different business.
Focus On The Data - Design Informed By Insights
These days, good UX design depends on having a deep understanding of how people act, what they like, and how they connect with things.
Designers can learn a lot about how people use a product or service by using data analytics and getting comments from users. This knowledge guides designers in making decisions that lead to interfaces that are not only nice to look at but also very useful.
Key Aspects
- User Research- Do a lot of user study to get to know the people you want to reach. To get both qualitative and quantitative data, use tools like polls, interviews, and analytics.
- User Persona Development - Based on your study, make detailed user personas. Personas are made up of stereotypes of typical users. They help designers make choices by giving data a face.
- Usability Testing - Usability testing should be done regularly to confirm design ideas and find places where things could be better. Real-life user testing is a great way to get feedback on how users feel about something.
Keep It Simple - Striving For Simplicity And Clarity
A crucial part of good UX design is keeping things simple. Users like intuitive, straightforward, and easy-to-understand interfaces.
A messy or complicated design can make people confused and angry, which is terrible for the user experience as a whole keeping things simple means making displays more straightforward to use, getting rid of things that aren't needed, and giving information clearly and concisely.
Key Aspects
- Minimalistic Design - Adopt a minimalist approach to design and stay away from extraneous details. A clean and uncluttered layout makes it easier for people to understand what they're doing.
- Clear Navigation - Focus on making navigation systems easy to use. People should be able to quickly find what they need without having to figure out tricky layouts or choices.
- Consistent Design Language- Use the same design style throughout the whole interface. Consistency helps people get used to something and speeds up the learning process.
Reduce Friction - Smoothing The User Journey
Any part of the user journey that makes it harder or takes longer to reach a goal is called friction. Getting rid of things that might get in the way of users' progress and making the experience smooth and fluid is what "reducing friction" means.
A smooth user journey not only makes users happier but also makes it more likely that they will do what you want them to do, like buy something or sign up for a service.
Key Aspects
- Streamlined Forms - Reduce the amount of required fields on forms to make them easier to submit. Set smart settings and make sure users know what to do.
- Efficient Onboarding - Optimize onboarding processes to familiarize users with a product or service quickly. To help people get used to the experience, give them tooltips, tutorials, or walks.
- Fast Load Times - Make it a priority for web pages and apps to load quickly. Users are more likely to give up on situations that take less time to load, which makes them think less of the product or service.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is UX In Business Terms?
In business terms, UX (User Experience) refers to the overall satisfaction and perception users have while interacting with a product, service, or brand.
What Is User Experience Also Known As?
User experience is also known as UXD (User Experience Design) or CX (Customer Experience).
What Is A User Experience In Business?
In business, user experience encompasses all aspects of a user's interaction with a company, from initial awareness to post-purchase support, influencing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
What Are Other Names For User Experience?
Other names for user experience include customer experience, digital experience, and strategic experience management.
Final Words
User Experience (UX) design is a meticulous process aligning design teams to create products that deliver meaningful experiences. Encompassing branding, style, and functionality, UX design is pivotal for user satisfaction and business success. Responsibilities extend beyond aesthetics, incorporating user research, testing, and optimization.
Collaborative efforts involve UX designers, product managers, developers, and support teams. The question persists: what is user experience called in business? It is the amalgamation of these efforts, a strategic approach placing the user at the forefront. In the dynamic digital landscape, businesses thrive when focused on crafting seamless, satisfying user journeys through effective UX design practices.