In the fast-paced realm of technology, acronyms often emerge, promising transformative shifts in the way we work and conduct business. What is XaaS and what can it bring to the digital workpplace? One such acronym that has gained prominence is XaaS, which is short for "Everything as a Service."
This paradigm shift transcends traditional models of software or infrastructure provisioning, ushering in a new era where various services are delivered over the Internet. This article explores the depths of XaaS and delves into the profound impact it can have on the digital workplace.
What Is XaaS?
The letters "XaaS" stand for "anything" in this acronym, as you may have guessed. Simply said, XaaS is the concept of providing "anything" as a service. It's a catch-all phrase for everything you can't physically have in your hands but instead get from a remote server or online, such as software, services, games, etc.
Microsoft Azure, many AWS offerings, and even Google Apps are just a few of the leading organizations that provide XaaS today. In fact, if you demand any IT services or computer-based capabilities, then you may receive them as XaaS.
All of these variants of cloud services are legal options from reputable vendors. However, there is a criminalized form of this presentation as well. Users subscribe to a service that gives them malware to launch assaults, making Malware as a Service (MaaS) a kind of organized criminality.
Key Features Of XaaS
XaaS thrives on its ability to provide tailored solutions. Organizations can customize services to fit their unique needs, ensuring that the digital workplace receives precisely the functionalities required.
This flexibility is a cornerstone of XaaS, allowing businesses to adapt swiftly to evolving requirements and stay ahead in the competitive digital landscape.
Cost-Efficiency Through Pay-as-You-Go Models
A defining feature of XaaS is its pay-as-you-go pricing models. This means organizations pay only for the resources they use, offering a cost-efficient alternative to traditional IT models. In the digital workplace, where demands can fluctuate, this approach ensures optimal resource utilization and cost-effectiveness, allowing businesses to scale up or down based on real-time needs.
Continuous Updates And Innovation
XaaS providers consistently roll out updates and innovations, ensuring that users in the digital workplace have access to the latest features and security enhancements.
This continuous improvement cycle eliminates the burden of manual updates, enhancing the overall user experience and keeping the digital workplace environment secure and up-to-date.
Global Accessibility And Connectivity
XaaS transcends geographical boundaries, fostering global accessibility and connectivity. In the digital workplace, this means that teams can collaborate seamlessly, regardless of their physical location.
The ability to access services and data from anywhere not only promotes remote work but also enables organizations to tap into a diverse talent pool, contributing to a more interconnected and inclusive digital workspace.
Scalability Without Limits
One of the standout advantages of XaaS is its unparalleled scalability. Digital workplaces often experience varying workloads, and XaaS allows organizations to scale resources up or down based on demand.
This elasticity ensures that the digital workplace remains responsive, efficient, and capable of meeting growing demands without the constraints of traditional IT infrastructure.
Unified Management Interface
XaaS often provides a unified management interface, simplifying the administration of various services. This centralized control allows for streamlined monitoring, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
In the digital workplace, this feature enhances efficiency, reduces operational complexities, and empowers administrators to manage diverse services from a cohesive platform.
XaaS And Digital Transformation Ain't A Done Deal
One way to advance digital transformation ambitions during tough economic times might be to take advantage of the recent proliferation of XaaS (anything-as-a-service). To alter a company's operations and business model using digital technology is known as digital transformation.
Given this gain, it would be reasonable to assume that businesses have already made significant progress toward their digital transformation goals. However, Statista predicts that worldwide investment in digital transformation will increase to $2.51 trillion in 2024 from the already-confirmed $1.6 trillion expenditure in 2022. There is little doubt that the transition to digital is continuing. The scope of the digital change makes this predictable.
- Adopting and incorporating cutting-edge technology like cloud storage, machine learning, the IoT, data analytics, and other cutting-edge tools.
- Decision-making that is "data-driven" is defined as "decisions, insights, and performance in business that are all based on data and analytics."
- Agile and cooperative: fostering a culture of creativity, teamwork, and responsiveness to market changes.
- Business process optimization entails eliminating redundant steps and reducing the need for human labor.
10 Types Of XaaS Businesses
The trend to as-a-service models is rising. According to a study conducted by KPMG in January 2023 among 600 organizations, this percentage has increased to almost 30% for corporate applications. By the end of 2024, these same companies anticipate that more than 40 percent of their corporate software will be hosted in the cloud.
The IT industry is making a global move toward SaaS models, which is worth billions of dollars. Millions of people all around the globe utilize various XaaS companies. Let's take a deeper look at some of the most popular ones.
SaaS (Software As A Service)
Most XaaS companies provide "Software as a Service," or SaaS for short. Businesses may save time and money by using SaaS solutions instead of building their custom software and integrating them into their existing IT stack.
In the end, it saves money and time for a firm, allowing its employees to focus on what really matters: running the business.
The typical business now employs 137 SaaS applications, up 30% from the previous year. This demonstrates the widespread use of integrated SaaS solutions across industries.
HubSpot is a well-known SaaS startup since it offers an integrated inbound marketing, sales, and service platform.
Kinsta is among the hundreds of thousands of companies that rely on this software to fuel their advertising campaigns. Its primary source of income comes from monthly subscriptions. HubSpot stores and manages its data on the cloud, as do the vast majority of SaaS providers today.
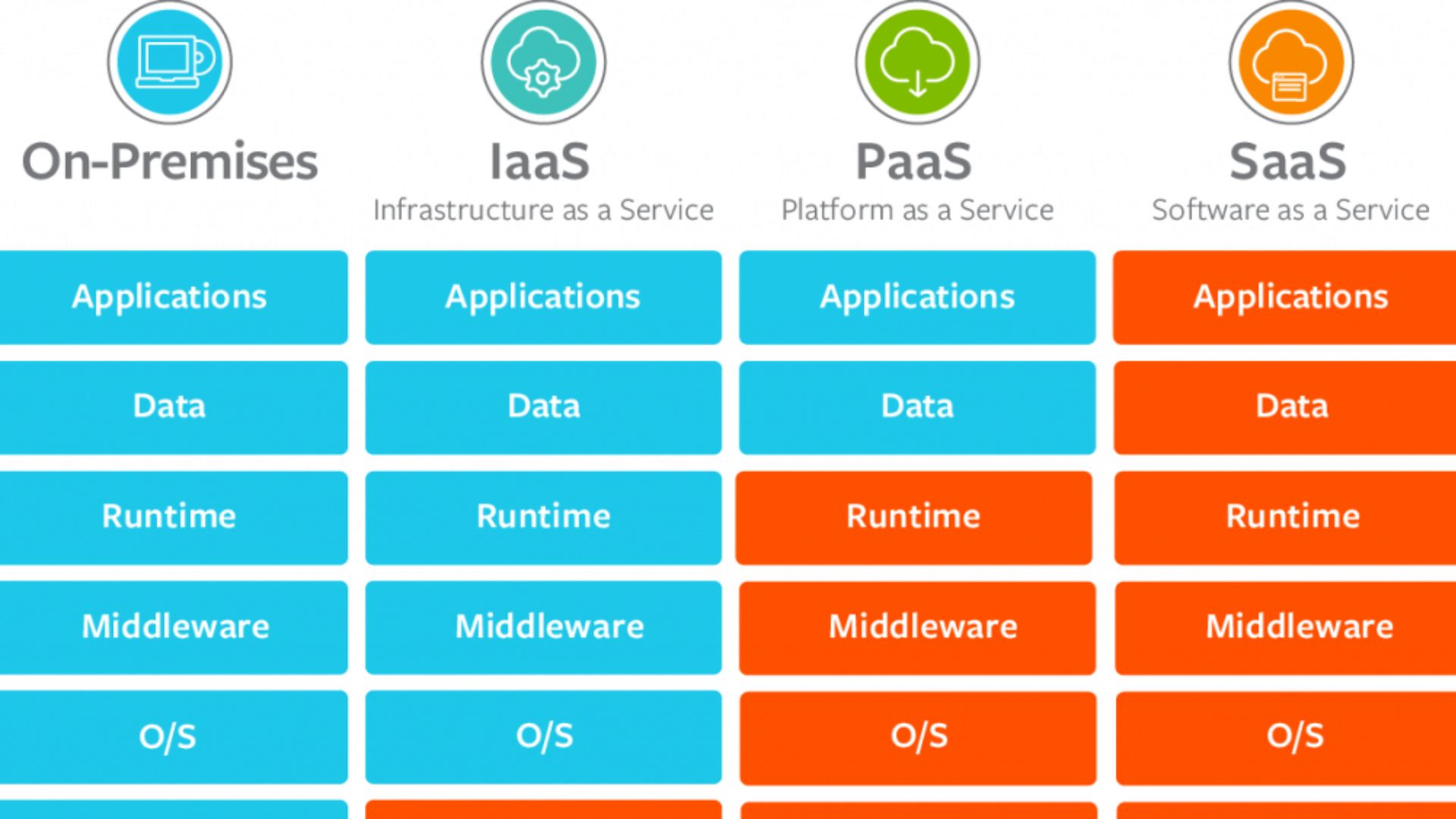
PaaS (Platform As A Service)
When you hear "PaaS," you think of "Platform as a Service." Instead of constructing their infrastructure from the ground up, PaaS providers give consumers a cloud-based alternative for developing their own applications, software, and other technical projects.
Providers of PaaS may provide their clients with anything from servers to data storage to database features and beyond.
The corporation owns the servers and the platform itself. Individually purchasing and storing hardware is unnecessary for users who construct their items on this platform.
AWS Elastic Beanstalk is an instance of a PaaS provider. By using AWS Elastic Beanstalk, businesses may "deploy and scale web applications and services on familiar servers."
PaaS offers a platform for entrepreneurs and company owners to construct goods on cloud-based infrastructure and sell them to the public.
IaaS (Infrastructure As A Service)
The acronym "IaaS" refers to "Infrastructure as a Service." Network-based solutions and data storage are examples of the types of infrastructure offered by IaaS providers. As a rule, they provide the processing power necessary to build, operate, and grow products.
If a business uses a PaaS platform to create its app or piece of software, then it will turn to an IaaS provider to keep it running and help it expand.
Most providers of IaaS operate on a "pay-as-you-go" basis, meaning that users pay only for the resources they actually utilize during a given period.
As the IaaS provider basically becomes your business's infrastructure, there is the risk of being utterly dependent on them. Your prosperity will be at the mercy of its dependability and uptime. Your business will be vulnerable if essential services are interrupted.
For instance, Microsoft Azure is an IaaS provider. Businesses can "build, manage, and deploy your applications anywhere" using Microsoft Azure. Scaling goods and businesses is now possible across all programming languages and frameworks.
AaaS (Analytics As A Service)
"Analytics as a Service" abbreviates the phrase "Analytics as a Service." Companies are converting data into insights and leveraging those insights to drive business choices. Companies are employing AaaS products to monitor crucial KPIs as they transition to digital solutions.
In 2019, the AaaS market was estimated to be valued at around $5 billion. Growth of over 25% every year is forecasted by experts until 2027. Companies that have mastered analytics will be better prepared to deal with whatever challenges they encounter.
Sisense is a firm that provides AaaS. Sisense is a robust analytics platform that enables the embedding of analytics to transform data into income. Once the technology has been successfully integrated, users may share data, do research, and work together to get new insights. There's no need to write any code to do this.
DaaS (Desktop As A Service)
The acronym "DaaS" refers to "Desktop as a Service." With the help of DaaS providers, businesses may oversee all of their staff from inside a protected web browser. When reporting to work, each employee would log in separately to that browser.
With this protected service, workers may quickly get remote access to work-related data, applications, and tools.
As more firms transition to remote working, DaaS solutions are in rising demand. By 2023, experts predict that the DaaS industry will be worth approximately $10.7 billion.
The necessity for enterprises to create specialized, regional desktops is reducing as a result of the versatility and dependability of DaaS solutions.
An example of a DaaS firm is Citrix. You and your staff may take advantage of Citrix's many remote-accessibility solutions. With Citrix Workspace, your team can collaborate more effectively across devices and operating systems by accessing the same set of programs and software from a single, secure desktop.
FaaS (Functions As A Service)
FaaS stands for "Functions as a Service." Suppose you needed to deploy a service or app but didn't want to create it from the ground up. A FaaS provider may assist with this.
Businesses may get access to specialized features or results via FaaS providers without shouldering the burden of applicationdevelopment or maintenance. The value of the rapidly expanding FaaS market is estimated at $7.5 billion.
An example of a FaaS firm is Google Cloud Functions. Google Cloud Functions is an elastic service that charges by the minute. In other words, it allows users to "run their code with zero server management."
In addition, it has debugging tools, support for hybrid and multi-cloud deployments, and security features.
STaaS (Storage As A Service)
The abbreviation "STaaS" means "Storage as a Service." Storing data in-house requires a lot of resources and time. This is why many businesses are looking to STaaS providers for their storage needs.
If you have a trustworthy STaaS partner, you may free up internal resources and save expenses by offloading specific data to them.
The STaaS market is the largest and most outstanding of all the XaaS types. By 2027, it is predicted that the global STaaS market will be valued at more than $100 billion. With more firms embracing cloud-based STaaS solutions to expand their operations, that number is projected to rise significantly in the years ahead.
HPE Greenlake is an organization that provides STaaS. HPE Greenlake is a division of Hewlett Packard Enterprise. It provides "cloud services for storage that are optimized for all your workloads."
The data platform provides all of its services as a subscription, making it very scalable.
CaaS (Containers As A Service)
The acronym "CaaS" refers to "Containers as a Service." All programs are stored in portable "containers" that may be opened and operated independently. The code, library, and dependencies are all put together in a container to be read and executed as required.
The CaaS model is similar to that of other XaaS providers in that it allows customers who don't want to create their container to store a code library to buy one instead. Forecasts put the value of the CaaS market at $4.1bn for 2019.
An example of a CaaS firm is Portainer. Portainer is a management solution that "allows anyone to deploy and manage containers without the need to write code." Many businesses may save significant amounts of time and money by contracting out the creation of their containers to a trustworthy third party.
DBaaS (Database As A Service)
DBaaS stands for "Database as a Service." With the help of DBaaS solutions, organizations may store client information in a centralized location where only authorized personnel have access.
With DBaaS, businesses can avoid the hassle of starting from scratch with their database. Instead, they may use a reliable DBaaS solution to build a database in the cloud that perfectly suits their needs.
Oracle Database is a DBaaS solution. To Oracle themselves, their database software, Oracle Database, is "the world's leading converged multi-model database management system." Connects MySQL, NoSQL, and in-memory databases.
Users are able to streamline their database operations and save time by collaborating across departments using this software.
AaaS (Authentication As A Service)
The abbreviation AaaS refers to "Authentication as a Service" in this context (as you can see, several abbreviations have more than one meaning). If there are other similar sectors (like "Analytics as a Service"), it may be necessary to be more specific about which business model you mean.
Access control solutions are one service that AaaS companies provide to their customers. It allows them to restrict product access to specific people or groups across all connected devices and networks. By 2026, analysts anticipate that the AaaS market will be worth $2.4 billion.
The company Duo Security is an excellent example of an AaaS provider. Duo Security offers "state-of-the-art access security built to protect every user, every device, and every application." Companies that use Duo Security might mandate that their staff use two-factor or multi-factor authentication.
Employees are required to take extra precautions to prevent unauthorized access to their accounts by verifying their login attempts.
Now that you're familiar with the various XaaS business models, it's time to examine why so many companies are adopting this strategy.
What Are The Benefits Of XAAS?
The expenditure model may be improved, new applications and business processes can be accelerated, and IT resources can be reallocated to more valuable initiatives thanks to XaaS.
- XaaS lets firms subscribe to services instead of buying them ahead, saving money. Before XaaS and cloud services, enterprises had to buy, install, and connect hardware, software, servers, security, and infrastructure to establish networks. Now, companies may use XaaS as needed and pay as they go. Operational expenses replaced capitalization costs.
- The idea lets companies quickly adapt to changing market conditions with new applications and operations. Multitenant cloud services may provide much-needed flexibility. Business owners and managers may swiftly scale up or down operations with resource sharing and flexibility aid. Rapid tech adoption permits smooth infrastructure growth to meet increased demand for cutting-edge services.
- IT resource allocation to high-impact projects IT companies are using XaaS to streamline procedures and free up resources for innovation. XaaS helps them digitize and become more agile. In a Deloitte research, 71% of companies said XaaS accounts for over 50% of their corporate IT. XaaS is democratizing innovation by making cutting-edge technology accessible to more people.
XaaS Challenges And Considerations
While XaaS models offer robust security measures, the inherent nature of cloud-based services introduces new security challenges. Data breaches, unauthorized access, and compliance issues become pertinent considerations for organizations embracing XaaS in their digital workplace.
Establishing a comprehensive security strategy and ensuring compliance with industry regulations are crucial steps in mitigating these risks.
Integration Complexity
As organizations adopt multiple XaaS services, the challenge of integration arises. Ensuring seamless communication and interoperability between different services can be complex. Integration challenges may lead to data silos, hampering the efficiency of the digital workplace.
Organizations must prioritize interoperability and invest in integration solutions to harness the full potential of XaaS without sacrificing cohesion.
Data Governance And Ownership
The distributed nature of XaaS often raises questions about data governance and ownership. When critical business data resides in external service providers' environments, clarifying responsibilities for data management, protection, and compliance becomes paramount.
Establishing clear data governance policies and contractual agreements with service providers helps organizations navigate these challenges and maintain control over their data assets.
Reliability And Downtime
While XaaS providers strive for high availability, occasional service disruptions can occur. Organizations must factor in the potential impact of service downtime on their digital workplace operations.
Developing contingency plans, leveraging redundant services, and assessing providers' historical reliability are essential steps in managing the risk of service interruptions and ensuring uninterrupted business continuity.
Cost Management
XaaS's pay-as-you-go model, while cost-efficient, can lead to unexpected expenses if not carefully managed. Organizations may face challenges in predicting and controlling costs, especially as usage scales.
Implementing robust cost management practices, monitoring usage patterns, and negotiating transparent pricing structures with providers is crucial to preventing cost overruns and maintaining financial control in the XaaS landscape.
Vendor Lock-In
Choosing XaaS providers offers flexibility, but it also introduces the risk of vendor lock-in. Organizations may become dependent on specific providers, making it challenging to switch services or adopt alternative solutions.
Mitigating vendor lock-in involves careful vendor selection, incorporating interoperability standards, and periodically assessing the landscape for emerging alternatives, ensuring that the digital workplace remains adaptable to evolving needs.
Performance Variability
XaaS performance can vary based on factors such as geographical location, network conditions, and provider infrastructure. Organizations may need more consistency in service performance, impacting the user experience in the digital workplace.
Employing performance monitoring tools, optimizing network connectivity, and collaborating closely with service providers are essential strategies to address and mitigate performance variability challenges in the XaaS environment.
FAQs
How Does XaaS Contribute To Workforce Agility In The Digital Workplace?
XaaS enables rapid scalability and resource allocation, fostering an agile environment where businesses can respond swiftly to changing demands.
In What Way Does XaaS Address The Challenge Of Resource Optimization In The Digital Workplace?
XaaS offers a pay-as-you-go model, ensuring cost-efficiency and optimal resource utilization by allowing organizations to scale resources based on real-time needs.
How Does XaaS Enhance User Experiences In The Digital Workplace?
XaaS provides continuous updates and innovations, ensuring that users have access to the latest features and security enhancements, thus improving overall user experiences.
What Role Does XaaS Play In Promoting Global Connectivity Within The Digital Workplace?
XaaS transcends geographical boundaries, fostering global accessibility and connectivity and enabling seamless collaboration among teams, regardless of their physical location.
How Does XaaS Contribute To Overcoming The Challenge Of Integration Complexity In The Digital Workplace?
XaaS integration challenges are addressed by prioritizing interoperability and investing in solutions that ensure seamless communication and cohesion among different services.
Conclusion
XaaS revolutionizes the digital workplace, offering tailored solutions, enhancing agility, and fostering global connectivity. The exploration of "What is XaaS and what can it bring to the digital workplace" encapsulates the transformative power of XaaS, symbolizing a shift towards a more connected, agile, and efficient digital future.